Female Reproductive System









Female Reproductive System
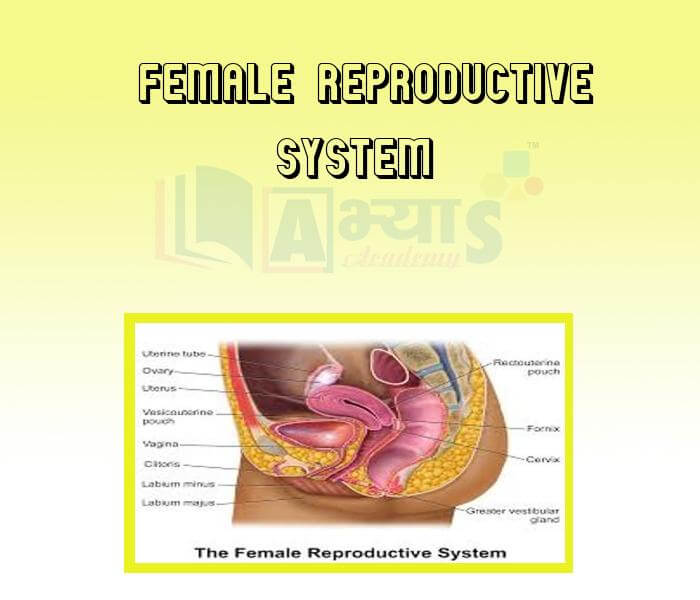
The female reproductive organs include the ovaries, Fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina and vulva.
Ovary: The ovaries are a pair of small, oval organs in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. They produce ova. At the time of birth, a female already has thousands of immature ova in her ovaries. Many of these degenerate during childhood. The ova start maturing when the female reaches puberty. Every 28 days, one of the ovaries releases an ovum. When an ovum is released from the ovary, it is taken up by a thin Fallopian tube (also called oviduct) through its funnel-shaped opening. The ovum is passed down the duct and into the uterus, which passes it out of the body through the vagina. The ovum is very small and, therefore, hardly noticeable.
Fallopian tube ( Oviduct ): The Fallopian tubes, or oviducts, are a pair of thin tubes that lead from the ovaries to the uterus. Each Fallopian tube has a funnel-shaped opening near the ovary. It is lined by cilia. The movement of the cilia helps conduct the ovum down the Fallopian tube and into the uterus.
Uterus: The uterus (womb) is a hollow, pear-shaped, elastic muscular structure. Its upper portion, into which the fallopian tubes enter, is broader. The narrow lower portion, called cervix, consists of a ring of muscles. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix. A fertilized ovum (zygote) develops into a baby inside the uterus.
Vagina: The vagina is a tube leading to the outside of the body through an opening called vulva. The vagina is the organ where the penis is inserted during intercourse for the discharge of sperms. It is also the passage through which the fully developed baby is born. The opening of the vagina in young female is partially closed by a thin membrane called hymen. The hymen is frequently ruptured in childhood due to strenuous physical exercise or disease.
Vulva : The external female genitalia is called as vulva.It contains independent opening of urethra and vagina. The sides of vulva has two small fleshy folds, the labia minora(lesser lips) which is hidden by larger hairy folds, labia majora(greater lips). These folds are equivalent of male scrotum. In the upper most angle of vulva in front of urethral opening is located,a small erectile clitoris which is highly sensitive and equivalent to male penis.
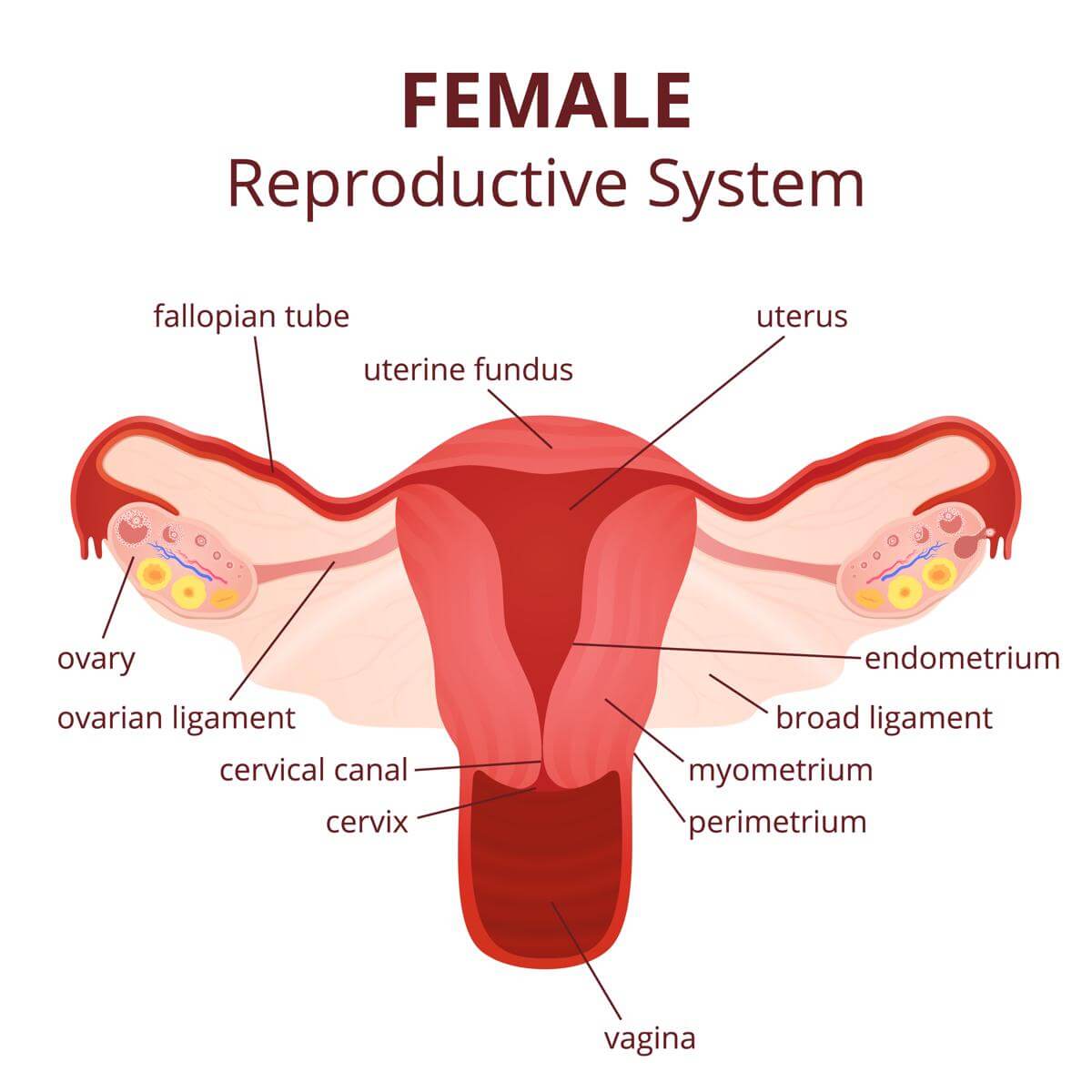
Ovaries: Ovaries are a pair of oval structures that are present one on either side. The ovaries produce eggs, one at a time, every alternate month, The eggs are produced by the germinal epithelial cells of the ovary.
Oviducts / Fallopian tubes
Oviducts / Fallopian tubes are a pair of tubes of about 12cm in length, They run from the ovaries of each side to the uterus. At the ovarian end the tube is funnel-shaped with the end of the tube thrown into number of folds. These folds are ciliated which help to sweep the egg produced by the ovary into the fallopian tube. The fallopian tubes are the sites for fertilisation of the egg by the sperms,
Uterus
Uterus is pear-shaped structure, broader on the upper end and narrower on the lower end. The upper end is called the body of the uterus and the lower end is called the cervix. At the upper end, it receives the oviducts of either side, whereas at the lower end the cervix opens into the vaginal canal that opens to the outside. The uterine wall has three layers. They are innermost endometrium made up of several glands and blood vessels, the middle myometrium made of smooth muscles and the outer perimetrium made of connective tissue. The inner surface of the uterus provides a site for the implanation of the embryo. The uterine wall plays an important role during childbirth. Cervix is made of sphincter muscle that controls the opening and closing of the uterus.
Vagina
Vagina is a 9cm long muscular tube that receives the penis during copulation. It is lined with epithelial cells. The secretions of the vaginal canal are acidic which is not conducive to the sperms as semen is alkaline. The vaginal opening in young females is partially covered with a thin mucous membrane called hymen. This is often broken early in females during play or strenuous work.
Vulva
Vulva is the external female genitalia. It comprises of the mons veneris, which is the raised pubis. The vaginal opening has two pair of folds on either side. The outer fold is thicker with hair, sweat glands and sebaceous glands and is called labia majora, The inner folds are thinner and devoid of hair. They are called labia minora. Covered by the upper part of the folds is the female equivalent of the penis called the clitoris. It is also an erectile and highly sensitive organ. In this region are two openings-the upper urethral meatus or opening and the lower vaginal orifice.
Development of foetus takes place in the ________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Development of foetus occur inside __________________ | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Given below are terms related to reproduction in humans. Pick the odd one. | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [20]
Abhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala Cantt area. The teachers of the institute are well experienced and very helpful in solving the problems of the students.The good thing of the institute is that it is providing extra classes for the students who are w...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas is an institute of high repute. Yogansh has taken admission last year. It creates abilities in child to prepare for competitive exams. Students are motivated by living prizes on basis of performance in Abhyas exams. He is satisfied with institute.

Yogansh Nyasi
7thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thMy experience with Abhyas Academy has been very good. When I was not in Abhyas whenever teacher ask questions I could not speak it confidently but when I came in Abhyas, my speaking skills developed and now I am the first one to give the answer of teachers question.

Upmanyu Sharma
7thWhen I have not joined Abhyas Academy, my skills of solving maths problems were not clear. But, after joining it, my skills have been developed and my concepts of science and SST are very well. I also came to know about other subjects such as vedic maths and reasoning.

Sharandeep Singh
7thThird consective year,my ward is in Abhyas with nice experience of admin and transport support.Educational standard of the institute recumbent at satisfactory level. One thing would live to bring in notice that last year study books was distributed after half of the session was over,though study ...

Ayan Ghosh
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thThe experience was nice. I studied here for three years and saw a tremendous change in myself. I started liking subjects like English and SST which earlier I ran from. Extra knowledge gave me confidence to overcome competitive exams. One of the best institutes for secondary education.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thWe started with lot of hope that Abhyas will help in better understnding of complex topics of highers classes. we are not disappointed with the progress our child has made after attending Abhyas. Though need to mention that we expected a lot more. On a scale of 1-10, we would give may be 7.

Manya
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very nice or it can be said wonderful. I have been studying here from seven class. I have been completing my journey of three years. I am tinking that I should join Abhyas Academy in tenth class as I am seeing much improvement in Maths and English

Hridey Preet
9thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala cantt.The institute provides good and quality education to the students.The teachers are well experienced and are very helpful in solving the problems. The major advantages of the institute is extra classes for weak...

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.
